

This chemical triggers the next molting cycle to prematurely develop adult structures, and can render most insects sterile if ingested in large enough quantities.Īgeratum houstonianum is toxic to grazing animals, causing liver lesions. Chemistry Īgeratum has evolved a unique method of protecting itself from insects: it produces a methoprene-like compound which interferes with the normal function of the corpus allatum, the organ responsible for secreting juvenile hormone during insect growth and development.
#Paintbrush plant family name full#
Preferring cool soils and exposure in full sun, high varieties reach stature heights up to 60 centimetres (24 in).

The species is cultivated once a year, having numerous varieties whose crowns may be dark blue, purple, pink and white. Today, it is widely used as an ornamental plant for summer borders and balcony boxes, high varieties also as cut flowers. Their habitat is pastures, moist forest clearings and bushes up to altitudes of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). It was also naturalized in large parts of the tropics and in the southern United States. The plant is native to Central America in Guatemala and Belize, and adjacent parts of Mexico, but has become an invasive weed in other areas. The flowering period is from May to November in the northern hemisphere. The narrow lanceolate bracts are pointed, denticulate only at the top and glandular hairy. The ray flowers are threadlike and fluff-haired, leading to the common name. The flower heads are borne in dense corymbs. This herbaceous annual or dwarf shrub grows to 0.3–1 m (1 ft 0 in – 3 ft 3 in) high, with ovate to triangular leaves 2–7 cm (0.79–2.76 in) long, and blue flowerheads (sometimes white, pink, or purple). The capsules are approximately 1/2 of an inch (9 to 12 mm) in length.Ageratum houstonianum, commonly known as flossflower, bluemink, blueweed, pussy foot or Mexican paintbrush, is a cool-season annual plant often grown as bedding in gardens. The leaves grow 1 to 4 inches (3 to 10 cm) in length.įruits: Capsules containing 2-cells and many seeds are produced. The margins of the leaves are usually entire, however the upper leaves may contain 3 shallow lobes with or without fine hairs. Leaves: Alternate, narrow, sharp-pointed linear to lance-shaped leaves are produced. The species name miniata is not related to the size of the plant, it is in reference to the scarlet-red color known as 'minium', which is an oxidation product of lead minerals. This species is our most common Castilleja in the mountains. When attempting to identify this species, look for the narrow un-lobed leaves, bright red inflorescence, sharply pointed calyx lobes, and greenish flowers which are much longer than the calyx. A perennial herb which produces small clusters of stems and grows in mountain meadows and grasslands, forest openings, on mountain slopes, and coastal bluffs.įEATURES: Castilleja is a difficult genus to identify. Broken plant parts have been used in the house for decoration.ĮDIBILITY: Yes. The plant has been used as hummingbird feed. A decoction of seeds has been taken as a cough medicine.
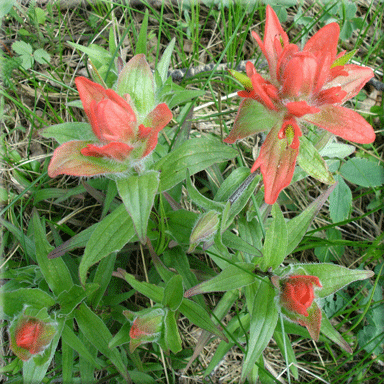
MEDICAL USE: The Gitksan, Nitinaht, and Nlaka'pamux Pacific Northwest tribes have taken a decoction of the entire plant to treat bleeding lungs, sore eyes, and backaches, as a diuretic and as a purgative. GENESIS NAME: Castilleja miniata Figwort FamilyĭISTRBUTION: East of the Rocky Mountains Alaska & Canada WEST FORK LAKE, MOUNTAIN 6416' & LOOKOUT TOWER TRAIL #347 TWO MOUTH LAKES TO THE WIGWAMS HIGH TRAVERSE SHORTY PEAK TRAIL #95 6515' & LONE TREE PEAK 6732' RUSSELL PEAK 6618' TRAIL #12 & RUSSELL RIDGE #92 MYRTLE LAKE 5950' & MYRTLE PEAK 7122' TRAIL #286 MOUNT ROOTHAAN 7326' AND CHIMNEY ROCK 7124' TRAIL #256 CUTOFF PEAK 6844' AND SMITH PEAK'S NORTH RIDGEįAULT LAKE 5980' & HUNT PEAK 7058' TRAIL #59


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
